Purpose of the flight and payload description
Is an instrument developed for mapping of the far-infrared emission from the Galaxy and external galaxies with the same spatial resolution as that of the IRAS (Infrared Astronomical Satellite) launched on 1983.
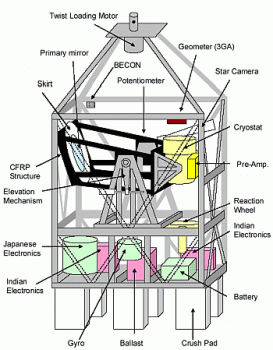
It has a telescope with an off-axis parabola glass mirror of 50 cm diameter and a focal length of 1200 mm. The instrument is mounted on the direct focus of this mirror. There is no other un-cooled optics. In order to reduce the instrumental infrared radiation noise from the periphery of the mirror, a ring-shape reflector is attached to the mirror.
Also was developed a far-infrared array camera dedicated for FIRBE. The array has 4 x 8 pixels, and the pixel pitch is 1.5 arcmin. The array uses stressed Ge:Ga photoconductor elements and is installed in a helium cryostat together with a cold reimaging optics.
The gondola on wich the instrument is mounted combines several aluminum pipes and angles, so FIRBE could be lighten the weight of the main frame less than about 100 kg, which also leads to reduce the total weight.
The telescope is deriven by an alt-azimuthal mounting system, the attitude stability is less than 30 arcsec. The attitude during the flight is determined with the data of three-axes fiber-optic gyro assisted by the CCD star camera and derived by a reaction wheel in azimuth and by a drive mechanism of a geared motor in elevation.
Details of the balloon flight
Balloon launched on: 12/3/1999 at
Launch site: TIFR National Balloon Facility, Hyderabad, India
Balloon launched by: National Balloon Facility, Tata Institute of Fundamental Research
Balloon manufacturer/size/composition: Zero Pressure Balloon
Flight identification number: 445
End of flight (L for landing time, W for last contact, otherwise termination time): 12/3/1999
Landing site: 53 km from Hyderabad, India.
Payload weight: 560 kgs
The balloon was launched from Hyderabad on December 3rd. 1999 by dynamic method assited by launch vehicle and auxiliary ballons.
After launch the balloon not reached float altitude and burst during ascent and the payload started coming down.
The payload descended to 2.4 km within 10 minutes in a free-fall manner and impacted in a point located at 53 km of Hyderabad in coordinates Lat: 17º 17' 25" Long.: 78º 5' 47".
From recovery, it had been inferred that the balloon failed to separate from the payload/load-line and the parachute had not deployed.
Most of the payload and the load-line equipments were completely damaged and then destroyed and decomposed by the native and some parts incinerated.
For this first flight in India were reconstructed the onboard equipments which received damages by falling into the sea in the 1998 flight and was modified the interface between Japanese electronics and Indian electric circuit.
There was no problem with the telescope system, wich could detect Jupiter as a reference source at the beginning of flight. However, due to the balloon burst the original observational plan was not meet.
External references
- Far-Infrared 160 µm Survey by Balloon-Borne Telescopes Star Formation, Proceedings of Star Formation 1999, held in Nagoya, Japan
- New balloon-borne telescope for far-infrared astronomy Proc. SPIE 4014, Airborne Telescope Systems, 237 (June 20, 2000);
If you consider this website interesting or useful, you can help me to keep it up and running with a small donation to cover the operational costs. Just the equivalent of the price of a cup of coffee helps a lot.