Purpose of the flight and payload description
This flight was part of the Joint Indo-U.S. Balloon Flight Program - 1961 a cooperative scientific launch campaign carried out between February and April 1961 by scientists from India and the United States in Hyderabad, India. The objective of the extended series of high-altitude balloon flights was to probe the tropical stratosphere using a wide variety of scientific instruments.
The objective of the flight was to collect samples of aerosols in the stratosphere to later measure the vertical distribution of fission products and natural radioactivities and of the size distribution of radioactive aerosols using the SMAC (Sub-Micron Aerosol Collector) a balloon-borne stratospheric sampling system developed by General Mills Inc. under contract with the Air Force Cambridge Research Laboratories (AFCRL).
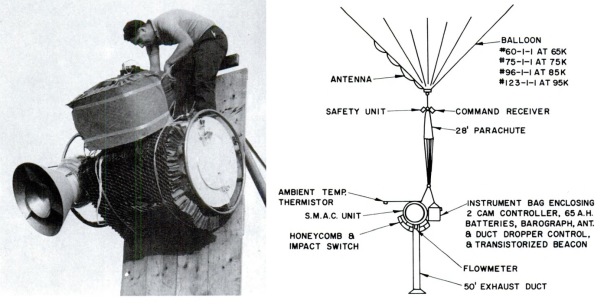
This air-filter unit used 10 square feet of polystyrene microfiber filter material produced by the Stanford Research Institute in a cylindrical configuration. The polystyrene fibers of the filter ranged from about 0.1 to 1.0 microns diameter allowing 100% collection efficiency for submicron aerosols over a wide range of particle sizes and flow rates. The prime air mover was an axial-fan blower mounted at one end of the housing so as to draw air through the filter drum at a sampling rate of over 1000 standard cubic feet of air per hour and exhaust it through a 50 ft duct suspended below the system to prevent air recirculation. At the other end of the housing, a door opened at altitude and closes upon completion of sampling. At left we can see the unit being prepared for flight and a detail of the complete balloon flight train (click to enlarge).
Two identical series of four flights were performed three weeks apart during the campaign, to altitudes of 65.000 ft, 75.000 ft, 85.000 ft and 95,000 ft. First series took place in March and second in early April. The individual flights on each series were made on nearly consecutive days, and floating altitudes were chosen day by day to afford the best flight conditions in relation to the high-altitude winds. The profile mission was to ascent to the particular floating altitude at a rate of rise of 1.000 feet por minute and to operate the SMAC unit at maximum altitude for periods of 80, 100, 120, and 150 minutes with increasing altitude. Also to telemeter time-altitude, ambient temperature, and sampler pump rpm.
Details of the balloon flight
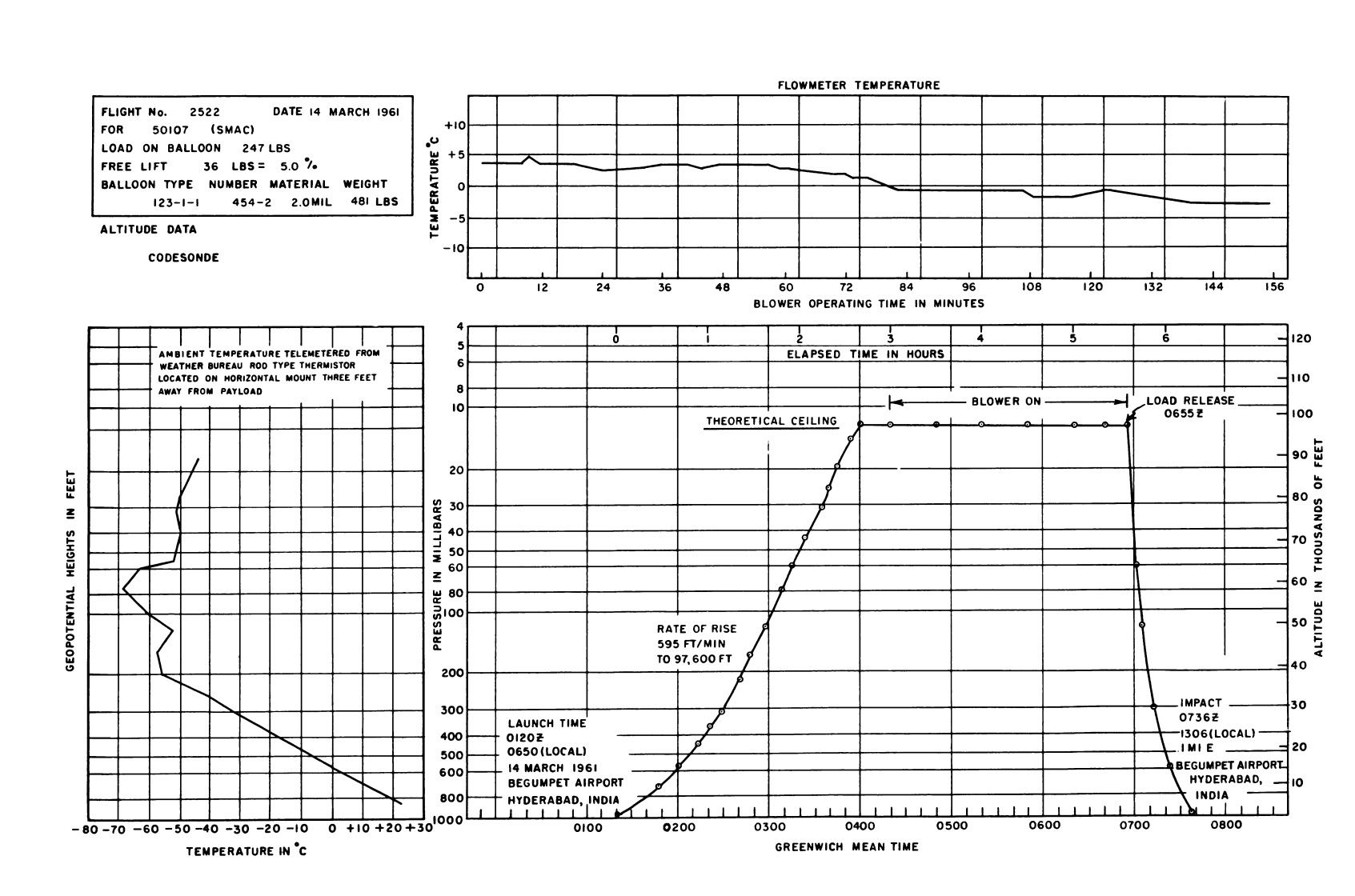
Balloon launched on: 3/14/1961 at 1:20 utc
Launch site: Begumpet Airport, Secunderabad, India
Balloon launched by: General Mills Inc.
Balloon manufacturer/size/composition: Zero Pressure Balloon General Mills 123-1-1 (2.0 mil)
Balloon serial number: 454-2
Flight identification number: GMI Nº 2522
End of flight (L for landing time, W for last contact, otherwise termination time): 3/14/1961 at 7:36 utc (L)
Balloon flight duration (F: time at float only, otherwise total flight time in d:days / h:hours or m:minutes - ): 6 h 16 m
Landing site: 1 Mile E Begumpet, Hyderabad, India
Balloon was launched on March 14th, 1961 at 6:50 local time from Begumpet Airport, near Secunderabad using dynamic method. Rate of rise to 97,600 ft was 595 fpm. SMAC Blower operated 155 minutes. Descent then began by parachute. The tracking aircraft still did not have ADF equipment but the crew was able to maintain visual contact with the parachute during the entire descent. The balloon had ascended toward the north through the lower altitudes and then drifted about 25 miles south at the upper altitudes. Winds at float altitude once again carried the balloon system toward the north. The end result was that impact occurred 1 mile east of the launch point near the opposite end of the runway from which launch was accomplished 6 hr earlier.
External references
- Joint Indo-United States Balloon Flight Program - 1961 Scientific Report - Air Force Cambridge Research Laboratories (U.S.) - 1962
If you consider this website interesting or useful, you can help me to keep it up and running with a small donation to cover the operational costs. Just the equivalent of the price of a cup of coffee helps a lot.